In just a few days, SpaceX’s next Starlink mission has gone from a complete mystery to a firm launch date.
Set to be SpaceX’s first Starlink launch in almost two months and first East Coast Starlink mission in almost half a year, the launch effectively came out of nowhere with a single week’s warning. For mostly unknown reasons, after completing an unprecedented 13 Starlink launches carrying almost 1000 satellites into orbit in the first five months of 2021, SpaceX has launched just one more batch of Starlink satellites in the last five months. Initially, mid-year, a brief delay of a month or two was expected as SpaceX prepared to debut the next generation of Starlink satellites on the West Coast.
Without explanation, that pause soon ballooned to four months and Starlink launches from Florida unexpectedly ceased in the meantime. Finally, on September 14th, SpaceX completed its first dedicated West Coast Starlink launch, delivering the first 51 new laser-linked Starlink V1.5 satellites to orbit. Again, oddities continued to abound in October as a second West Coast Starlink launch initially scheduled mid-month was delayed indefinitely – and remains so almost a month later.
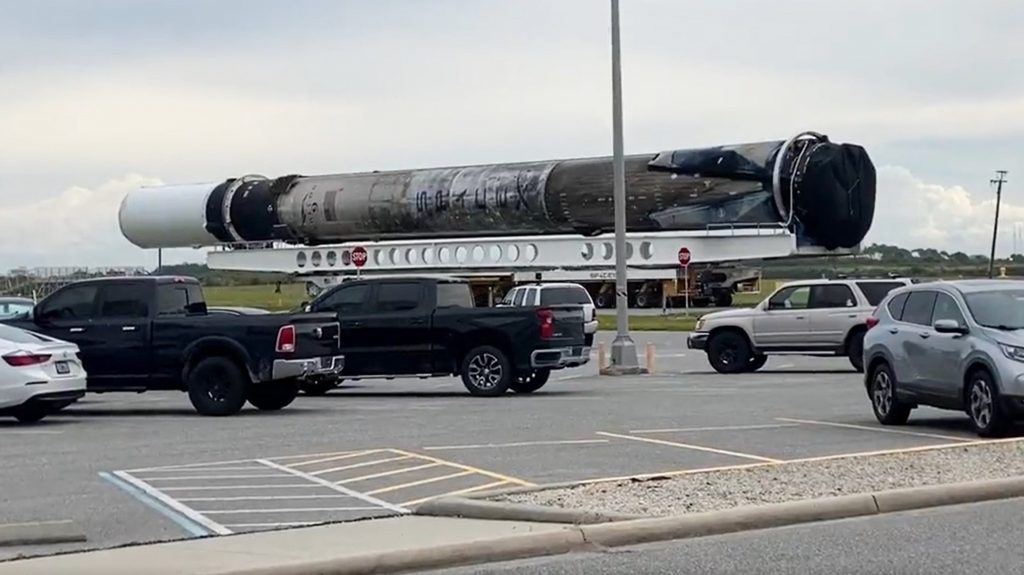
As of just a few days ago, SpaceX still had no Starlink missions with firm launch dates. However, on November 4th, a sooty Falcon 9 booster (B1062) with a shiny new second stage attached was spotted rolling down Kennedy Space Center (KSC) road on its way to SpaceX’s other Cape Canaveral LC-40 pad. Given that Pad 39A was already occupied with a Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft scheduled to launch four astronauts as early as November 10th and that the next mission clearly on SpaceX’s East Coast manifest was more than a month away, a surprise Starlink mission was the only obvious explanation.
Indeed, just a day after that surprise rocket transport, hazard areas published by the Cape Canaveral’s 45th Space Wing confirmed that SpaceX had scheduled a Starlink launch no earlier than (NET) 7-8am EST (12-13:00 UTC) on Friday, November 12th. Oddly, instead of the polar “Starlink 2-2” launch most observers were expecting, the range hazard area announcement was for a mission called “Starlink 4-1,” raising further questions about SpaceX’s new naming scheme.
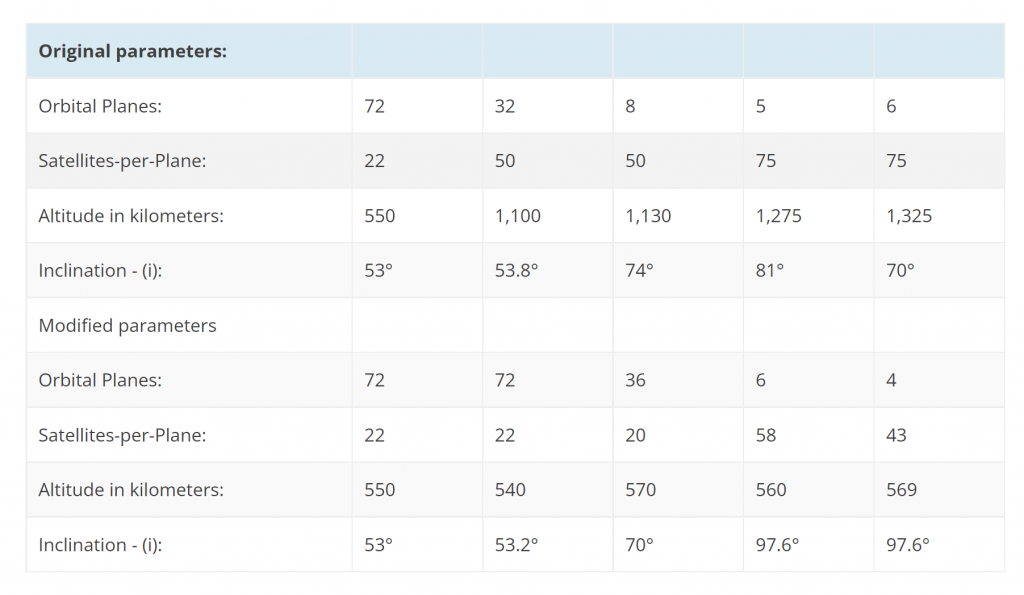
In simple terms, the first ~4400-satellite phase of SpaceX’s Starlink constellation is split into five groups of satellites – known as shells – with different orbital altitudes and inclinations (the orbit’s tilt). In May, SpaceX’s most recent East Coast Starlink launch effectively completed the first of those five shells. With Starlink V1.5’s September debut, SpaceX also debuted a new naming scheme, deeming the mission Starlink 2-1 – the first launch of the second shell. Based on the inclination implied in Starlink 4-1’s hazard warning, Shell 4 refers to a second group of 1584 satellites almost identical to Shell 1, while Shell 2 is a semi-polar group of 720 satellites. That means that Shells 3 and 5 are sets of either 340 or 158 satellites at slightly different altitudes in polar orbit and will likely be the last Phase 1 Starlink satellites SpaceX launches.
Unlike Shell 1’s Starlink V1.0 satellites, Shell 4 is expected to use Starlink V1.5 satellites with laser interlinks that will eventually allow the constellation to route communications entirely in orbit, limiting the need for ground stations that are both expensive and a bureaucratic nightmare to construct and operate.
Serving as a final confirmation of the imminent Starlink launch, SpaceX service ship Bob departed Port Canaveral with drone ship A Shortfall of Gravitas (ASOG) under tow on November 7th, joining drone ship Just Read The Instructions – already at sea for Crew-3 booster recovery.


I love how you addressed this issue. Very insightful!